A
B
ADR (Accord Dangereux Routier)
European regulations established by the UN treaty in 1957 (in force until today) specifying the rules that must be followed by the logistics industry when transporting hazardous goods by land.
ASN (Advanced Shipping Notice)
The full information on the expected delivery. It contains details of the physical characteristics of the shipment, for example, size, weight, mode of transportation, and carrier information, so the customer can be ready to receive and accept it.
The ASN is a notification usually sent electronically via EDI – electronic data interchange or as an XML file.
ASP (Average Storage Period)
The information specifies the period in which the inventory (and therefore the capital) is stored in the warehouse.
These data allow you to work on increasing the efficiency of the company by working on faster sales of items; ASP is calculated on the basis of the inventory turnover versus the number of days in a year.
ATA (Actual Time of Arrival)
The opposite of ATD (Actual Time of Departure). The exact time it takes for the loaded transport to reach its destination.
ATD (Actual Time of Departure)
The opposition to ATA (Actual Time of Arrival). The exact time at which any form of transportation (ship, airplane, etc.) is actually moving with the packed cargo from the place of departure.
Back-order
An order that has been placed for a product or service that is currently not available. From the retailer's point of view, stocks should be replenished shortly, on a particular date.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
What back-order is and how to deal with it during high season 2021?
BOPIS (Buy Online, Pick up In-Store)
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Buy Online Pickup in Store (BOPIS) – an opportunity or a challenge?
Branding (in terms of packaging possibilities)
Bundling (packaging)
Bundling (product)
Combination of several products in one package. Sometimes, when a few items are merged, the result is a new item with a separate SKU (Stock Keeping Unit). This is often a seasonal feature, e.g., Christmas sets, and specific to certain industries, e.g., beauty care collections or baskets of sweets.
C
D
Cabotage
The right to provide transport services by land, sea, or air - within a specific country.
Carbon footprint
A term used to describe the sum of greenhouse gases produced by our activities (individually, during specific events, or as a country, an industry, a company). The carbon footprint is expressed as carbon dioxide equivalent.
You can read more about this topic in the posts below:
Carbon offsets
The action taken to compensate for the production of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases during various activities. They are usually sold in defined quantities according to a scheme. For example: Buying a carbon offset worth X will allow planting new trees.
You can read more about this topic in the posts below:
Carrier
A company or legal entity with authorization to provide transport services by air, water, or land.
Carrier liability
A document specifying the scope of the carrier's liability for the loss or damage of the goods during transport - with the exception of those caused by force majeure, public enemy, public authority, actions of the sender, or the inherent nature of the goods.
Category management
A type of strategic management of product clusters used in the retail trade industry. It allows for quick response to consumer demands thanks to real-time insight into the state of product categories.
CBM (Cubic Meter)
The measure of volume used by transporters to calculate the chargeable weight. To calculate the volume of a shipment you multiply the following values in meters: length, width, and height.
CEP (Courier, Express, and Parcel Services)
A term primarily applicable to regional postal companies that handle small and light mails (letters, small packages) on a daily basis.
It concerns the limitation of dimensions and weight of parcels delivered by these entities, allowing for automated handling and sorting of parcels, which has an impact on delivering them more efficiently and in a shorter time.
Chargeable weight
CKD (Completly Knock-Down)
COD (Cash On Delivery)
CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
Software that allows improvement of establishing and maintaining relationships with customers at every stage of their service process: from creating lead profiles, through updating the lists of acquired customers, to communication management.
Cross-border logistics
Area related to the transport of goods between countries across the globe. It provides a safe and constant flow of goods in the supply chains in compliance with the applicable international regulations and taxes.
You can read more about this topic in the posts below:
Cross-border strategy for eCommerce
How to start cross-border sales as a small/mid-size eCommerce?
D2D (Door-to-Door delivery)
Type of shipment, which is collected from the hands of the vendor and delivered directly to the ordering party's door - excluding e.g. warehouses etc.
DAP (Delivered At Place)
Dark stores
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid)
Duty
Or Custom Duty. Taxes or tariffs imposed on parcels that cross national borders in the shipping process.
You can read more about this topic in the posts below:
5 top factors that affect shipping costs (and how to reduce them)
Dead stock
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Declared value
Delivery notification
Distribution logistics
Also called sales logistics. A logistic system that takes care of the planning, implementation, and control of the movement of goods.
DOD (Delivery on Demand)
Simply saying, a situation in which the product is being delivered when it's' needed. For example, a car component is delivered when it is to be mounted on a vehicle to be folded.
Double blind shipment
DPP (Damage Protection Plan)
A kind of extra insurance for containers delivered by container leasing companies. It covers certain types of damage or maintenance costs of the leased premises.
Dropshipping
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
E
F
Economy of scale
The efforts of companies to achieve business efficiency by placing an emphasis on increasing production while reducing its costs - which are divided into a greater number of goods.
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange)
Type of electronic communication in the supply chain that enables the transfer of data. The system speeds up order processing and responses to customer inquiries.
EDI is a direct computer-to-computer communication method that eliminates the use of traditional email, fax, and postal service.
ETA (Expected Time of Arrival)
The expected time in which the order will reach its' final destination.
ETD (Expected Time of Departure)
Express delivery
The fastest shipping form. The buyer bears additional costs for his selection in return for a guarantee of receiving the package from 24 to 72 hours from the time of ordering.
Fast-moving Items
Also called products with a high turnover rate - items sold frequently, in a short period of time. They do not require long storage (less than 3 months) and usually take up little space.
FEFO (First Expired, First Out)
One of the methods of managing goods in stock. The products with the shortest expiry date leave the warehouse first. The method is most often applied to perishable products, mainly in the food industry.
FIFO (First In, First Out)
Method of stock management. Goods that enter the warehouse first are also the first to leave it. This prevents a situation in which a batch of goods is left over in the warehouse.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Fifth-Party Logistics (5PL)
Logistics service providers sometimes referred to as logistics aggregators. It carries out the planning, organisation, and improvement of its customers' logistics processes. It often manages several supply chains and negotiates rates on behalf of multiple parties.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
First-Party Logistics (1PL)
The term refers to a company that carries out its logistical needs in-house. Otherwise known as self-logistics.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
First Tier Supplier
Flash sales
Fourth-Party Logistics (4PL) or Lead Logistics Provider
Type of logistics operator. It takes the role of a manager in the entire logistics process and is the single point of contact for all parties involved. It supports the organization and optimization of the whole supply chain.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Fragile goods
This term is used for delicate products that are prone to breaking or damage, such as glass, porcelain, musical instruments, enamel, ceramics and others. Should be treated with special care during storage and transport.
Fulfillment or Order Fulfillment
The entire order handling process, from the moment the order is received until delivery of goods to the customer. This process includes several stages such as storage, picking, packing, shipping, and returns management. It can be carried out in-house or outsourced, usually to a third-party logistics company.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
What’s fulfillment all about...?
What is omnichannel fulfillment?
Grow your business with ecommerce fulfillment
10 reasons to consider fulfillment services for your ecommerce
Fumigation
A process allowing to get rid of pests from packages prior to shipment to their final destination. Particular attention is paid to it in international transport thanks to import-export regulations. It applies to both the transport of wood and pallets, as well as... recycled packaging.
G
H
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices)
An international system that confirms that the manufactured goods comply with quality standards and that the production process is controlled. These are the minimum requirements that a manufacturer must meet in order to prove that his products are of high quality.
It concerns mainly those elements which are difficult to eliminate in the final product, such as contamination, labeling, etc. These rules are checked by the relevant agencies issuing permits for production and sale in sectors such as food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements, or medical devices.
Gross weight
Hazardous materials (HAZMAT)
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
What do you need to know about shipping hazardous materials?
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points)
Handling costs
Price related to parcels' picking, packaging, and shipping costs. Ultimately, those costs should be the same or lower than the cost of the order fulfillment.
I
J
Inventory
All the items held or passed through your business, necessary for its trading activities.
You can read more about this topic in the posts below:
Guide to eCommerce inventory management
Real-time inventory management: benefits, tools, and strategies
Inbound logistics
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
In-house fulfillment
Entire eCommerce order processing is carried out in-house, using the available resources. This process includes several stages such as storage, picking, packing, shipping, and returns management.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
In-house transport
Product shipment law regulated by the Road Haulage Act - allowing to transport items at different locations within the same company, using vehicles and employees belonging to the mentioned brand.
JIT (Just-In-Time)
K
L
Last mile
The final stage of the logistic supply chain, i.e. the delivery of the package to the end customer. It is seen as one of the most important stages in the online ordering process.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Lean logistics
LIFO (Last In, First Out)
M
N
Minimum weight
The least weight at which goods will be transported by a carrier at a specified rate is usually applied to large quantities (as barge load, carload, or truckload).
Mixed load
Container filled with shipments of various contents in a single consignment.
Mode of transportation
Different ways of moving goods from one place to another, including both sea, land, or air, as well as pipelines (gas/oil transfer), space (satellite), and cable (internet and energy transportation).
NOR (Notice of Readiness)
No-read parts
O
P
OBC (On Board Courier)
An employee employed by a delivery company whose task is to transport express parcels by plane.
A product shipped in this way will never become a cargo parcel; it will always be under the care of a dedicated courier who will take care of it during the flight (he will check in for the flight with your shipment, will have it in the overhead locker and will be personally responsible for it until the very moment of delivery).
Omnichannel
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Order confirmation
A document confirming the receipt of the order task and its acceptance in the system.
OMS (Order Management System Software)
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Order Management System (OMS): Why is it important for e-commerce?
OOS (Out of Stock)
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Outbound logistics
Oversized shipment
Also known as heavy load shipment. The parcel in which the size or weight exceeds the maximum permissible dimensions permitted under the law of the country or territory where the part of the shipment or delivery takes place. Saying simply: a situation concerning shipping large items.
Overstock
Package or Parcel
One or more items in individual wrappings, packed in box, paper or foil, intended for shipment.
You can read more about this topic in the posts below:
Packaging costs vs. ecommerce profitability
Packaging (types, costs, common mistakes and best practices)
Partial Shipment or Split Shipment
This is a delivery of a single order in more than one parcel. This situation occurs when a product, for example, consists of several parts which cannot be sent in one shipment or when an order includes several products and some of them are not available at the moment (in this case we speak of backorders). Shipments are often delivered on different days.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
10 tips on how to prepare your ecommerce logistics for high season
Picking
Place of Destination
Specified place where the shipment has to be delivered. The moment when the parcel is delivered to the chosen location is the time when the carrier has fulfilled its part of the job.
Place of Origin
In logistics, the term refers to the place from where the package was picked up by the courier.
POD (Proof of delivery)
Predictive logistics
Term referring to logistical processes using the potential offered by artificial intelligence and big data analysis.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Procurement logistics
Production logistics
PSS (Peak Season Surcharge)
Variable surcharge applied by carriers during a period of increased deliveries (season peaks), most frequently for shipments from Asia. It happens between June and October.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
10 tips on how to prepare your ecommerce logistics for high season
Q
R
Quality assurance
One of the elements of quality management. These are all systematic and planned activities that aim to ensure that the manufactured product meets the set quality requirements.
These actions are taken to prevent mistakes during production and to avoid problems related to the delivery of defective products to the market.
Qcommerce
Quick commerce, is a model based on rapid delivery of products in a maximum of one hour after placing the order. The most popular among grocery e-shops.
Reverse logistics
Reverse Logistics process in dynamic e-commerce growth
Fulfillment for industry: Cosmetics
In Linker Cloud we can also support your reverse logistics: ⬇️
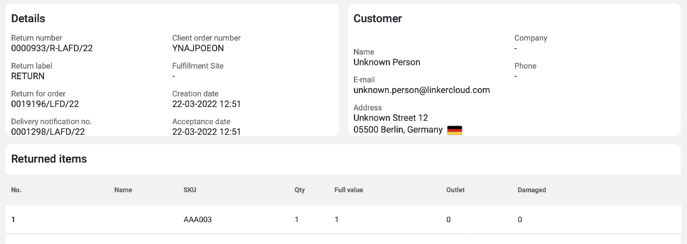
For more on this topic, check out our Tech Overview post.
Return Delivery Note
Form completed by the customer to return part or all of the products ordered. It contains detailed information about the products such as name, quantity, price. Together with the receipt, it helps to speed up the return process.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Reverse Logistics process in dynamic e-commerce growth
In Linker Cloud we can also support your reverse logistics: ⬇️
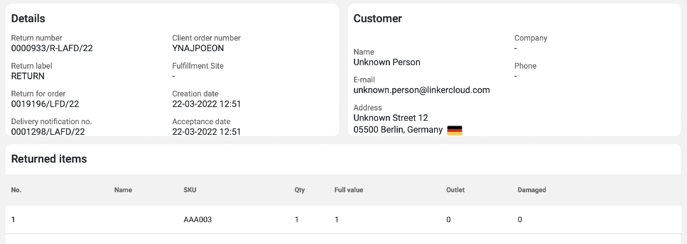
For more on this topic, check out our Tech Overview post.
Returns policies
A document setting out the rules in which retailers describe when and how buyers can return unwanted or defective products previously purchased online.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Retailer
Person or company that sells goods to individual customers in stores or online shops, not to other stores or companies.
Reseller
Company that buys products to resell, not for its own consumption. This also includes companies that buy goods from manufacturers and sell them to customers.
Real-time inventory
Specialized software that allows automating the process of recording the sales and inventory management, thus influencing faster response to changes appearing in supply chain.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Real-time inventory management: benefits, tools and strategies
S
T
Seasonal demand
Predictable, increased demand for goods or services in commerce, caused by special events. Usually associated with religious holidays such as Christmas, annual events such as Women's Day or Valentine's Day, and weather or periods of the year that raise demand for specific products.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
10 tips on how to prepare your ecommerce logistics for high season
Scalability
Attribute of an organisation, system, model or function that describes its ability to manage an increased scope of operation or work. In relation to business, it means the development of activities, increasing the scale of operations on many levels.
SCM (Supply Chain Management)
Management of the flow of all goods and services within the business's supply-side activities. It includes all processes in the production cycle, from raw materials to finished products. Well-managed supply chain optimise costs and increase business efficiency.
SCV (Supply Chain Visibility)
The service provided by the technology manages the supply chain, tracking product orders, components and finished products as they move between suppliers, manufacturers and the end customer. The purpose of this is to enhance the supply chain, as information on stocks, orders and deliveries is easily accessible to any entity.
Second-Party Logistics (2PL)
The type of logistics service provider. It owns or leases transport equipment providing transport and delivery services only.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Shipment
Usually, large quantities of products shipped together to a selected destination or simply the act of shipping goods (including single items).
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
5 top factors that affect shipping costs (and how to reduce them)
SKU (Stock Keeping Unit)
Slow-moving Inventory or Slow-moving Items
Spare Parts Logistics
Carried out to eliminate delays due to defective components in transport equipment or machinery involved in the logistical process. Rapid replacement of parts avoids delayed deliveries, reducing additional costs. This process is particularly important when spare parts are difficult to obtain.
Staging area
The area used for the temporary storage of goods in a warehouse. Such areas may be used for various purposes, e.g. they may held products that are ready to be placed in the warehouse or products that have been collected and are ready to leave the warehouse.
Stock transfer
Means the movement of goods from one link in the supply chain to another. Usually the transfer of stocks to another warehouse.
Storage
Supply Chain
It is the set of processes involved in the production and distribution of goods and services, ensuring their flow between the producer, suppliers, and end customers. The supply chain is an essential element of competitive advantage - the better it is optimised, the greater the benefits for the business.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Supplier
3PL (Third-Party Logistics)
The most popular model of the logistics service provider combines warehousing and transportation.
The company provides logistics services such as transport and delivery, storage, order picking, packing, shipping, or handling returns.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Tracking
The term refers to systems and methods for tracking goods throughout the supply chain. It helps to determine where products and materials are located and how they are going to be managed.
Trade logistics
A term used to describe all logistical processes taking place in a company related to both the flow of materials, goods, and the flow of information.
These are processes that occur in relation to customers, suppliers, and producers, inside and outside the organization.
Traffic management
One of the most important elements of logistics. It is about planning, organizing, and purchasing transport services that enable to transfer of freight.
This process includes e.g. shipment consolidation, carrier selection, rate negotiations, or document preparation.
Transaction costs
Expenditure incurred for the purchase or sale of goods and services.
Transaction costs are not included in production costs, they are made at the stage of transfer of the product (sale) from one entity to another.
Transfer order
Transit time
The time needed for the shipment to reach its final destination after pick-up from the sending point. Typically measured in hours or days, depending on the transport method selected.
Transport of dangerous goods
A special type of consignment, treated with extra care. The mode of transportation and requirements vary depending on the classification of the dangerous product.
In most cases, special packaging, appropriate labeling, and additional documents are required. These shipments incur higher costs.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
What do you need to know about shipping hazardous materials?
Transportation
The movement of people, animals, and goods from one place to another. There are four basic forms of logistic transportation: road, rail, maritime, and air shipments.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
U
V
Unit cost
UPC (Universal Product Code)
The first barcode commonly used worldwide to track products sold in a shop. First used in Canada and the USA.
The full version consists of 12 digits combined with the machine-readable bar code, which is unique for each product. A short version of UPC consists of 6 digits.
Upselling
A sales strategy that encourages the customer to buy a higher version of a product than the one initially selected by the customer in order to increase revenue.
This could mean a newer model of the product or one that is upgraded.
VAL (Value Added Logistics)
Extension of logistic services by additional solutions, increasing the value of performed services, in areas related to storage or specialized transport.
This results in services tailored to the customer's needs.
VAS (Value Added Services)
Extension of services by additional solutions, such as e.g. storage, packaging, labeling.
This results in services tailored to the customer's needs, which translates into greater flexibility and reduced costs.
Vendor
A term referring to a person or company that sells particular products or services.
In the supply chain, a vendor is understood as a goods provider, less often as a manufacturer and supplier.
VMI (Vendor Managed Inventory) or VOI (Vendor Owned Inventory)
Management of the supplier's stocks. This is a type of supply chain outsourcing. There are three parties involved in this process: the supplier, the buyer, and/or the logistics operator.
Thanks to the fact that the buyer gives information about demand the supplier can provide the right amount of materials at the optimum time and to the desired location.
W
X
Waiting costs
An additional charge is made when the time allocated for loading and unloading the goods is exceeded. In the case of container transport, this time is usually 2 hours. The cost arose as a result of having to wait for loading or unloading.
Warehouse
The commercial building used for the storage of goods. It is used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, retailers, logistics and transport providers, etc.
Warehousing is one of the key elements of the supply chain.
You can read more about this topic in the post below:
Waste management logistics
Waybill (UIC)
Document issued by the carrier containing detailed information on the shipment, such as the sender and recipient, place of destination, place of shipment, route.
Wholesaler
Individual or company that buys and sells large quantities of goods, usually to retailers or other business entities.
WMS (Warehouse Management System)
XYZ analysis
A term is also known as XYZ inventory management.
A type of analysis that helps categorize product stocks according to the variability of their demand.